Seamless credit accessibility support farmers to Improve Agriculture practices
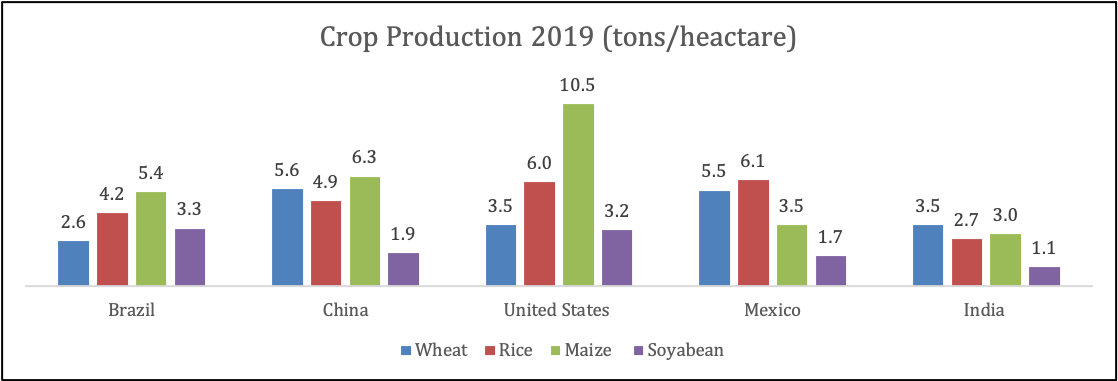
India is an agricultural country with 58% of the population depending on agricultural income (Indian brand equity Foundation (IBEF) data). Despite having the tenth largest cultivable land, our food grain production is lower than countries such as China, Brazil, and The United States for varieties of major crops.
This is because of several reasons like Uncertain climatic conditions, dependency on monsoon, drought, low mechanization levels, financial literacy, and limited access to formal finance. Finance for Agricultural purposes plays a vital role as it provides support to the farmers for better access to seeds, fertilizers and Agri equipment, resulting in increased agricultural productivity.
Agricultural loans can be obtained for multiple purposes.
- Working capital loans for buying seeds & fertilizers
- Terms loans for purchasing agri machineries for farm mechanization
- Crop storage construction
- For agri allied activities like, dairy, poultry, fisheries
- Buying agricultural land, land reclamation and development
Let us look at some of the ways in which agricultural loans can support farmers.
- Increase in productivity
It is common knowledge that a farmer who produces more will sell more and subsequently will earn more. However, the sector needs a robust plan to put this plan into action. The farmers need to find a buyer who agrees to buy the entire produce, otherwise resulting in heavy losses due to yield damage. Selling all the produce to the nearest mandis, multi-retail brands or processing units could get farmers a great return, but it is essential to be cautious.
To increase production, farmers need to adopt the latest farm technologies that help in increasing the crop yield from the same land. If the farmers do not have ready funds to purchase such equipment, taking credit from formal financial institutions like Banks/ NBFCs is the advisable solution. The credit will be useful in buying, machinery, cattle, irrigation equipment, etc. The farmers can also avail the term/ investment loans from various banks and financial institutions in India.
Providing seamless access to the credit will help the farmers to invest adequate resources and support them to increase crop production. The increased crop could be sold to either multiple buyers or the same buyer, resulting in more revenue in their hands. It is not necessary to revamp the entire business model or find new buyers to accomplish these goals.
- Diversifying produce
Another innovative way to earn more profits is crop diversification. Most farmers are accustomed to producing the same crops year over year, and it works for them. However, they need to realize that crop rotation is great for the soil, and crops like vegetables, fruits and other perishable goods fetch higher prices than conventional crops.
Along with selling the farm produce to a broader client base, agricultural loans also help farmers to ensure proper crop storage by assisting the farmers to build storage spaces and prevent wastage. Case in example, India produced about 291.5 tonnes of wheat in 2019-20 out of which 4-6% was lost due to improper storage. This means at least 13 – 18 million tons of food-grains were destroyed which is not acceptable for a country like India having more than 120 crore population to feed. With proper financing, farmers can invest in storage facilities, tools, Agri machinery, irrigation like drip irrigation, etc. to meet their agricultural requirements. Exploring the available financing options in the market and knowledge would go a long way to build a sustainable storage infrastructure to reduce crop wastage. Speaking to experts if necessary and choosing the best loan type suited for the business need is the key.
- Post-harvest expenses
Once the farmer harvests the crops, they might want to reap the benefits of higher yield. Storage and logistics and complete supply chain management for the crop from the farm to the end customers are essential for the Agri produces to command the right price. The public domain statistics suggest Indian farmers experience post-harvest losses of around INR 93,000 crores.
Post-harvest wastage can be reduced by picking the crops at the right stage. Information about seeds, harvesting, watering techniques, etc. is important to reduce such losses. Analyzing the water quality by using test strips to check the chlorine content, checking the water temperature, monitoring the farm labor that harvests the crop is familiar with the correct technique are some of the paramount steps for higher yield. Cuts or gashes can destroy the crop/fruit and allow moisture, insects to creep in and ruin it and hence storing the Agri produces under the right temperature is an important aspect too.
- Produce marketing
Often farmers are forced to sell their produce at a lower price because of several reasons like fear of spoilage, market conditions, lesser demand, etc. When they are forced or unwilling to sell at a lower price, it severely impacts their profits, and it turns out to be a bad year for the farmers. Produce marketing loans prevent distress sale of farmer’s produce.
Produce marketing loans helps pay farmer’s existing loans and dues and provides the liquidity support to meet emergency financial needs. Such loans are offered against agricultural receipts and produce stored in the warehouse. The loan amount can be 60 to 80 percent of the Agri produce (depending on the storage) value. Repayment duration depends on the crop type or geographical location. When the circumstances are favorable, the farmer can sell his produce at the right price and heave a sigh of relief.
- Value chain financing
Not every year is a profitable year for farmers. Due to uncertain circumstances like floods, droughts, storms, crops get destroyed, leading to heavy losses to the farmers. A loan could prove useful as it can help farmers cover operational costs and feed their families. Value chain financing is a great way to minimize risk and maximize profits.
Such solutions could be implemented in Agri and allied sectors like dairy & poultry. In value chain financing, relevant value chain stakeholders are involved which depends upon crop or locations. The financiers analyze the risk by taking all value chain players and implement risk mitigation solutions which act as an enabler for growth. Sometimes the collateral acquired by financiers is through the relationships established in the value chain.
Payment deduction at the source implemented under value chain financing can help farmers sell their produce to multiple buyers at the same time. Financiers provide loans to farmers by obtaining transactional comfort from the buyer of the produce. Under the arrangement, the buyer deducts the loan repayment due by the farmer from the payment to be made post realization of the produce.
- Reduced operational hassles
Agricultural loans take care of a farmer’s credit needs at various stages of agriculture. Right from buying seeds, fertilizers to harvest, there are different kinds of loans. Each loan is for a specific purpose.
Quick processing time, minimal paperwork and adequate security options provided by any financier make it easy for the farmer to obtain loans that can be both long-term and short-term loans. The ease and convenience take the stress off the farmers for their credit requirements, so that they can focus on farming. Lastly, there are no hidden charges. All the fees are paid upfront.
Conclusion
Agricultural loans can help boost a farmer’s income by making their life easier, enabling them to manage risks better and handle emergencies without any stress. It is crucial to choose the right loan for the right purpose. Ensuring that repayment terms match their cash inflows, and they can honor their installments commitments timely to the financier. If not paid on time, the farmer’s credit score will be downgraded which in turn will reduce their capacity to avail any loans in the future.
References-
- https://data.oecd.org/agroutput/crop-production.htm
- https://www.chintan-india.org/sites/default/files/2019-09/Food%20waste%20in%20India.pdf
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/small-biz/sme-sector/indian-farmers-face-rs-93000-cr-post-harvest-loss-e-commerce-can-address-such-pressing-challenges/articleshow/77558911.cms